Chapter 2 | Bits, Data Types, and Operations¶
- Bit, Binary digit, codes
- Data type
- unsigned integer
- signed integer
- logical variable
- floating point number
- ASCII code
Definition
BIT
- 0 and 1 are binary digit
- BIT stand for Binary Digit
Data Types
Each ISA has its own set of data types and its own set of instructions that can operate on those data types.
Signed Integer¶
2's complement 二补数,补码
- Given n bits, 2's complement can only represents 2n numbers, \(-2^{n-1} \le x \le 2^{n-1} - 1\)
- Make sure, say that -3 + 3 = 0
| 0000 | 0 |
|---|---|
| 0001 | 1 |
| 0010 | 2 |
| ... | ... |
| 0111 | 7 |
| 1000 | -8 |
| 1001 | -7 |
| ... | ... |
| 1110 | -2 |
| 1111 | -1 |
OVERFLOW¶
- the case like -4 + -5 = +7, but not -9
SIGN EXTENSION¶
Different bits number operate together, which isn't work.
For example, a 4-bit number plus a 8-bit number. So we should turn a 4-bit number to 8-bit number.
- Method to turn, which is called SIGN EXTENTION
- if positive, add 0 at the front
- if negative, add 1 at the front
| binary | decimal |
|---|---|
| 01001100 | 76 |
| 11111011 | -5 |
| 01000111 | 71 |
Conversion between Binary and Decimal¶
\((21.79)_{10} \approx (10101.110)_{2}\)
Logical Variable¶
It can be represented by 1 bit.
Logical FUNCTIONs¶
- NOT
truth table
| x | f(x) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 |
- OR
truth table
| INPUT COMBINATION | ||
|---|---|---|
| x | y | f(x, y) |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
- AND
truth table
| INPUT COMBINATION | ||
|---|---|---|
| x | y | f(x, y) |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
De Morgan's Laws
- XOR / Exclusive-OR
truth table
| INPUT COMBINATION | ||
|---|---|---|
| x | y | f(x, y) |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
- XNOR / Exclusive -NOR Equivalence
truth table
| INPUT COMBINATION | ||
|---|---|---|
| x | y | f(x, y) |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
BIT VECTOR¶
It is an m-bit pattern where each bit has a logical value independent of the other bits.
Usage¶
- A bit mask
- Managing a complex system made up of several units, each of which is individually and independently either busy or available
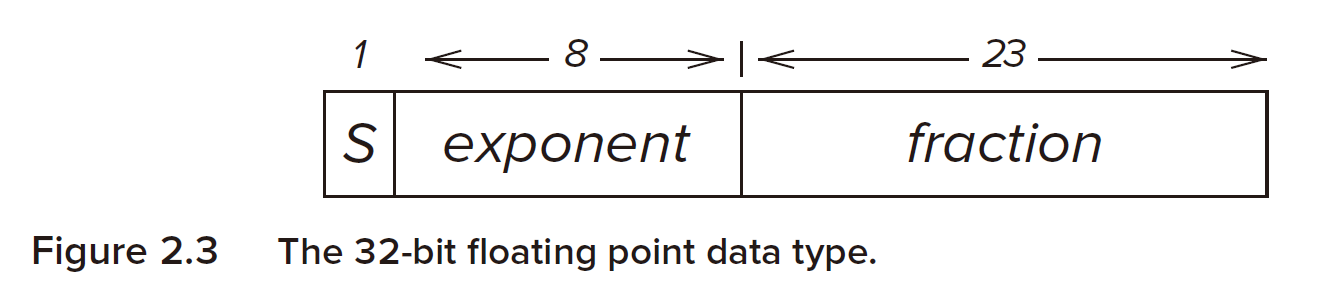
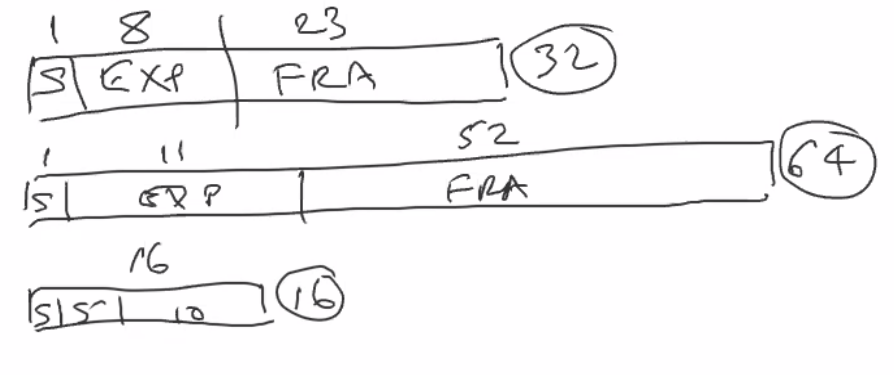
Floating Point Number¶
or say scientific notation in other science field.
32-bit floating point
| BIT Length | Sign | Exponent | Fraction |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8-bit | 1 | 5 | 10 |
| 16-bit | 1 | 8 | 23 |
| 32-bit | 1 | 11 | 52 |
ASCII code¶
ASCII stands for American Standard Code for Information Interchange.
It's only used for information trasmittions between I/O devices and computer.
Hexadecimal Notation¶
创建日期: 2024.02.21 00:56:50 CST